internal tibial torsion test|how to assess tibial torsion : manufacturers With internal tibial torsion, the shin bone (tibia) is slightly twisted or rotated, causing the foot to turn in. This may be due to the position your child was sitting in while in the uterus. Intoeing due to internal tibial torsion is generally most . 15,000+ FREE Online Slots Games to Play - Play free slot machines from top providers. Play with no download, no deposit, or registration!
{plog:ftitle_list}
webGameGuardian is an all-in-one application developed for android video gamers to manage their video games. This application includes certain advanced features and options to be used in video games. Therefore, some people find it is not that straightforward to use the GameGuardian APK with mobile games. Download GameGuardian DOWNLOAD .
Internal Tibial Torsion is a common condition in children less than age 4 which typically presents with internal rotation of the tibia and an in-toeing gait. Diagnosis is made clinically with a thigh-foot angle > 10 degrees of .Internal torsion causes the foot to adduct, and the patient tries to compensate by everting the foot, externally rotating at the hip, or both. Similarly, persons with external tibial torsion invert .Tibial torsion is the twisting of a child’s shinbone, also known as the tibia. In most cases, tibial torsion causes a toddler’s legs and feet to turn inward (internal tibial torsion), giving them a pigeon-toed appearance. Less often, the legs turn . Internal tibial torsion A1,A2,A11–A14. Presents between 2 and 4 years of age. Affects boys and girls equally. Most common cause of intoeing, usually presenting in toddlers
With internal tibial torsion, the shin bone (tibia) is slightly twisted or rotated, causing the foot to turn in. This may be due to the position your child was sitting in while in the uterus. Intoeing due to internal tibial torsion is generally most .
The diagnosis of tibial torsion is made by a history and physical examination by your child's doctor. During the examination, the doctor obtains a complete prenatal and birth history of the .Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. This condition causes a child to have inward-facing toes and bowed legs. It may be caused by the position of the baby in the uterus. A physical exam can diagnose tibial torsion. .
are the princeton review tests harder for ap exams
The three most common causes of intoeing (i.e., metatarsus adductus, internal tibial torsion, and increased femoral anteversion) initially should be managed conservatively with serial.
Internal tibial torsion is common at birth, but it typically resolves with growth. However, an excessive degree of torsion may indicate a neuromuscular problem. Torsion also occurs with .Craig's test is a passive test that is used to measure femoral anteversion or forward torsion of the femoral neck. It is also known as 'Trochanteric Prominence Angle Test (TPAT)'.[1] . high FAA results in a shorter abductor lever arm and also considerably increases internal rotation moment length. Reduced FAA results in higher shear forces on . internal tibial torsion (toddlers) Pathophysiology. a packaging disorders caused by intra-uterine positioning. most spontaneously resolve by age 10. . trochanteric prominence angle test . patella internally rotated on gait .
Dr. Rome explains how to look for tibial torsion, or tibial rotation, with the knee at a 90 degree angle. Special thank you to Dr. Matthew Rome and Equilibri.
Dr. Rome explains the proper technique to determine if a patient exhibits any degree of external tibial torsion.Special thank you to Dr. Matthew Rome and Equ. Disability from lateral tibial torsion is usually caused by patellofemoral instability and pain. 9 Therefore, lateral tibial torsion is a more common indication for osteotomy than internal torsion .Internal tibial torsion is one cause of intoeing. With internal tibial torsion, the shin bone (tibia) is slightly twisted or rotated, causing the foot to turn in. This may be due to the position your child was sitting in while in the uterus. Intoeing due to internal tibial torsion is generally most noticeable when a child begins walking.Tibial torsion occurs if the child's lower leg (tibia) twists inward. This can occur before birth, as the legs rotate to fit in the confined (limited) space of the womb. After birth, an infant's legs should gradually rotate to align properly. If the lower leg remains turned in, the result is tibial torsion.
Drexler et al conducted a study to evaluate the clinical and radiographic outcomes of 12 patients (15 knees) undergoing tibial derotation osteotomy and tibial tuberosity transfer for recurrent patella subluxation associated with excessive external tibial torsion. [] Clinical evaluation was carried out using preoperative and postoperative Knee Society Score, Kujala . Internal tibial torsion is most frequently bilateral, and may at times present with metatarsus adductus, femoral anteversion, or physiologic bow legging. Pertinent clinical findings on examination include a forward or outward-facing patella, or in a seated position, there may be a posterior rotation of the medial malleolus (in comparison to the .
Internal Tibial Torsion External Tibial Torsion Metatarsus Adductus Pediatric Foot Cavus Deformities . and forefoot adduction. A coleman block test is useful to assess for the flexibility of the hindfoot deformity to assist with surgical planning.Internal tibial torsion is common in children aged under four years old. It typically presents as internal rotation of the tibia and in-toeing gait. It often resolves spontaneously by four years of age; less than 1% of torsional deformities fail to resolve in childhood. . Craig's test: also known as the Trochanteric Prominence Angle Test.Internal tibial torsion usually corrects itself in the first 6 to 12 months of walking. If the internal tibial torsion alone is 40 degrees at any time, or persists beyond 6 to 12 months of walking, consider having your child seen by an orthopedist for evaluation and possible treatment.Tibial torsion can be external (lateral) or internal (medial). (See also Introduction to Congenital Craniofacial and Musculoskeletal Disorders.) External tibial torsion occurs normally with growth: from 0 ° at birth to 20 ° by adulthood. External torsion is rarely a problem. Internal tibial torsion is common at birth, but it typically .
may exhibit positive 'cover-up test' often associated with internal tibial torsion. leg length discrepancy. usually NO tenderness, restriction of motion, effusion. lateral thrust on walking. Imaging. Radiographs . views. ensure that patella are facing forwards for evaluation (commonly associated with internal tibial torsion) The etiology of intoeing (i.e., metatarsus adductus, internal tibial torsion, and increased femoral anteversion) is debated, although the causes generally can be correlated with the patient's age . Free EKG Test Congenital Heart Surgery Real Time Outcomes ℠ News Videos Meet the Team Patient Stories Request an Appointment . Also known as: internal tibial torsion, intoeing. What is tibial torsion? When the tibia bone of the leg twists inward in children, it can lead to tibial torsion. This is also commonly called intoeing, and it is a .
are the sat chem practice tests harder than real
Create Personal Test Create Group Test Enter Test Code . Internal Tibial Torsion External Tibial Torsion Metatarsus Adductus . > 10° of internal rotation is indicative of tibial torsion (normal is 0-20° of external .
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Internal tibial torsion is a normal developmental variation., _____ are the shortening and hardening of muscles, tendons or tissues leading to fixated and stiff joints., Treatment modalities to promote mobility include _____, pharmacologic management, and surgery. and more.
While most torsional deformities may not affect a child’s function, abnormal tibial torsion may exacerbate foot deformities. For example, internal tibial torsion in a child with residual clubfoot may cause them to trip excessively. Excessive ETT in a child with cerebral palsy exacerbates the proximal femoral anteversion deformity. 12. Foot . This test distinguishes tibial torsion from femoral anteversion, where the mismatch between internal and external rotation persists both in hip flexion and extension . The 3 most commonly described techniques to specifically measure tibial torsion are the thigh-foot angle (TFA), the transmalleolar axis (TMA) ( 35 ) and the second toe test ( 36 .The tibia can either twist inward, called internal tibial torsion, or outward, called external tibial torsion. Males and females are affected equally. Cause. Internal tibial torsion can occur before birth when the legs internally rotate to fit in the womb, as early as 7 weeks into fetal development. It can be associated with tibia vara or a .
are the sat practice tests harder than the actual test
Furthermore, a new technique called the second toe test was proposed to measure tibial torsion . Although physical examination has advantages, physical measurements have disadvantages such as lack of reproducibility. . Internal derotation osteotomy of the tibia: pre- and postoperative gait analysis in persons with high sacral myelomeningocele .Create Personal Test Create Group Test . Internal Tibial Torsion PMID: 5047787 Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1972 Jul-Aug;86:183-6. D 2 FREE PDF. Tibial torsion: a method of assessment and a survey of normal children. . In this report, a simple clinical method of assessing tibial torsion by calculating the transmalleolar axis is presented. The .External tibial torsion occurs normally with growth: from 0 ° at birth to 20 ° by adulthood. External torsion is rarely a problem. Internal tibial torsion is common at birth, but it typically resolves with growth. However, an excessive degree of torsion may indicate a neuromuscular problem. Torsion also occurs with Blount disease. Persistent .
Internal tibial torsion is associated with medial meniscus posterior horn tears . support that arthroscopic DMM results in joint degeneration in the Yucatan minipig and provides a new large .
Tibial Torsion What is tibial torsion in children? Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. These bones are located between the knee and the ankle. Tibial torsion causes a child’s feet to turn inward. . Know why a test or procedure .
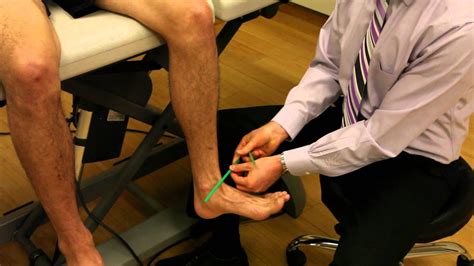
tibial torsion special test
29 de jan. de 2023 · Trans, irmãs Mayla Phoebe e Sofia Albuquerck nasceram em MG, passaram por cirurgia em SC e moram, respectivamente, na Argentina e em SP. Ambas .
internal tibial torsion test|how to assess tibial torsion